Leader

Task 1
To study the impact on cancer immunosurveillance of JAK inhibitors (JAKi) and other anti‑inflammatory biologic drugs, in vitro, ex vivo and in silico
To study the impact on cancer immunosurveillance of JAK inhibitors (JAKi) and other anti‑inflammatory biologic drugs, in vitro, ex vivo and in silico.
There is a higher incidence of cancer in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with JAKi versus anti‑TNF. This allows to analyze the mechanisms leading to cancer in autoimmune diseases.
The laboratory has already explored this question through its work on NK cells, showing that JAKi impair NK‑cell activation and degranulation, ultimately reducing their ability to kill cancer cells. This first line of evidence suggests that JAK‑STAT inhibition may weaken several layers of tumor immunosurveillance.
Building on these findings, Samuel Bitoun and Audrey Paoletti analyze how JAKi act on the immunosurveillance of T cells, B cells, monocytes and monocyte‑derived macrophages, to obtain a comprehensive view of how these drugs reshape antitumor immunity.
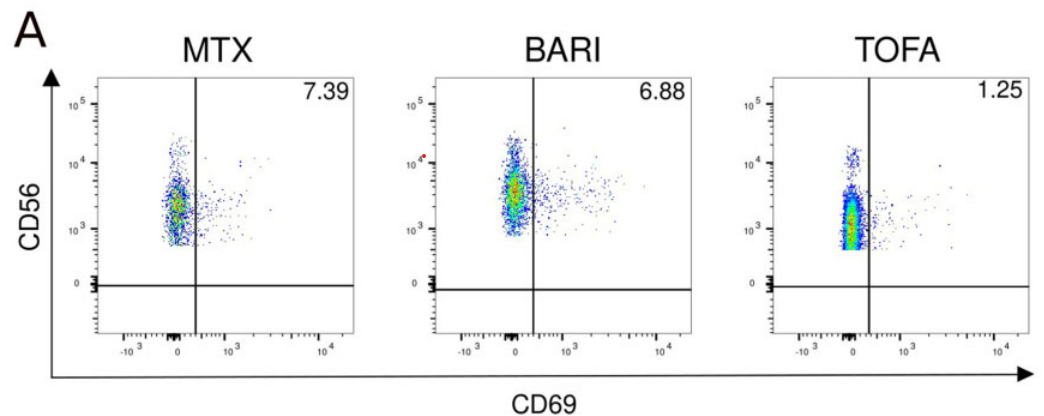
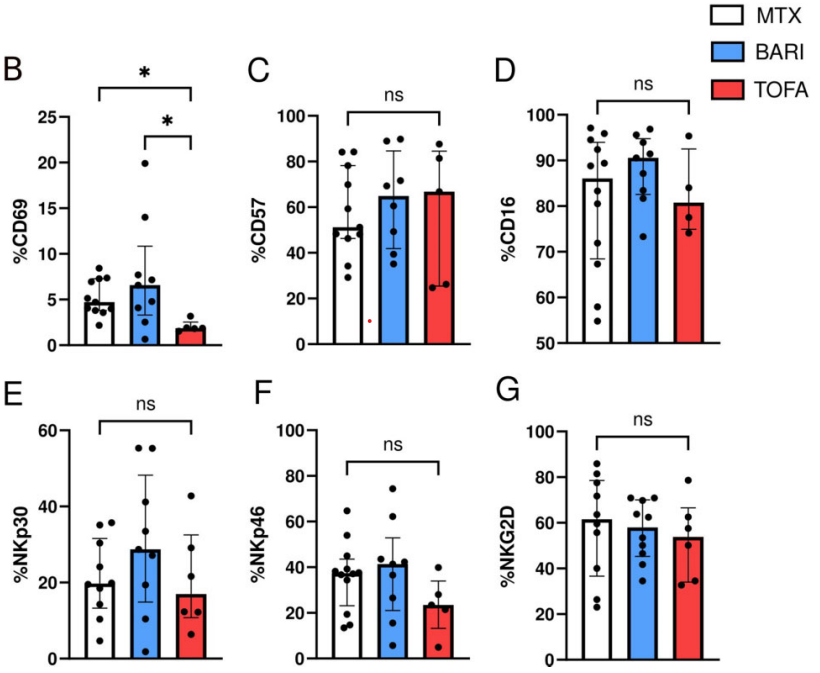
NK cell phenotypes in RA patients treated with TOFA, BARI or MTX. NK cells from RA patients treated by MTX (n = 12), TOFA (n = 6) and BARI (n = 10) were phenotyped. (A) FACS plot of the effect of JAKi on CD69. Comparisons of the expression of (B) CD69, (C) CD57, (D) CD16, (E) NKp30, (F) NKp46 and (G) NKG2D between MTX, BARI and TOFA. Results are shown as median (IQR). Kruskal–Wallis test was used. *P < 0.05
Read the full scientific article : Janus kinase inhibitors alter NK cell phenotypes and inhibit their antitumour capacity
Task 2
To decipher the transition between autoimmunity and lymphoma in the model of Sjögren’s disease and to find new biomarkers of this transition
Sjögren’s disease is the autoimmune diseases with the highest risk of lymphoma with an increased risk of 10 to 15-fold compared to the general population. Progression from autoimmunity towards B-cell lymphoma in Sjögren’s disease is a multistep process. Gaëtane Nocturne has proved that lymphoma in Sjögren’s disease results from hyperactivation of B cells, notably of auto-reactive rheumatoid factor (RF) B cells, and from defective control of inflammation. Our aim here is to understand which factors promote B-cell overactivation and to decipher the role of immunosurveillance in lymphoma occurrence. We have found that patients with lymphoma may have a genetic predisposition to this complication. FHU CARE² assess whether germline abnormalities in genes involved in NF-kB pathway favor B cell escape and we develop a short list of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) able to refine the risk of lymphoma. In addition, FHU CARE² track specific at-risk RF clonotypes in Sjögren’s disease patients with lymphoma and evaluate the evolution of these clonotypes over time.
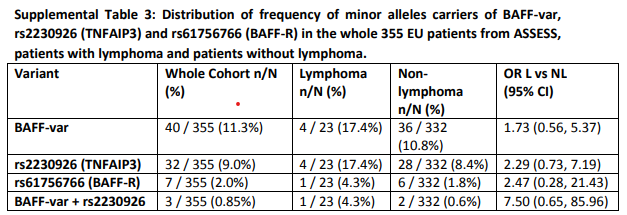
Read the full scientific article : A genetic variant of BAFF is associated with the risk of lymphoma in Sjögren disease.
Read the full scientific article : The Lancet Rheumatology : Machine learning to classify the focus score and Sjögren’s disease using digitalised salivary gland biopsies a retrospective cohort study.
Task 3
To compare in vitro the effect of immunomodulators for Immune-Related Adverse Events post immune checkpoints (ICI)
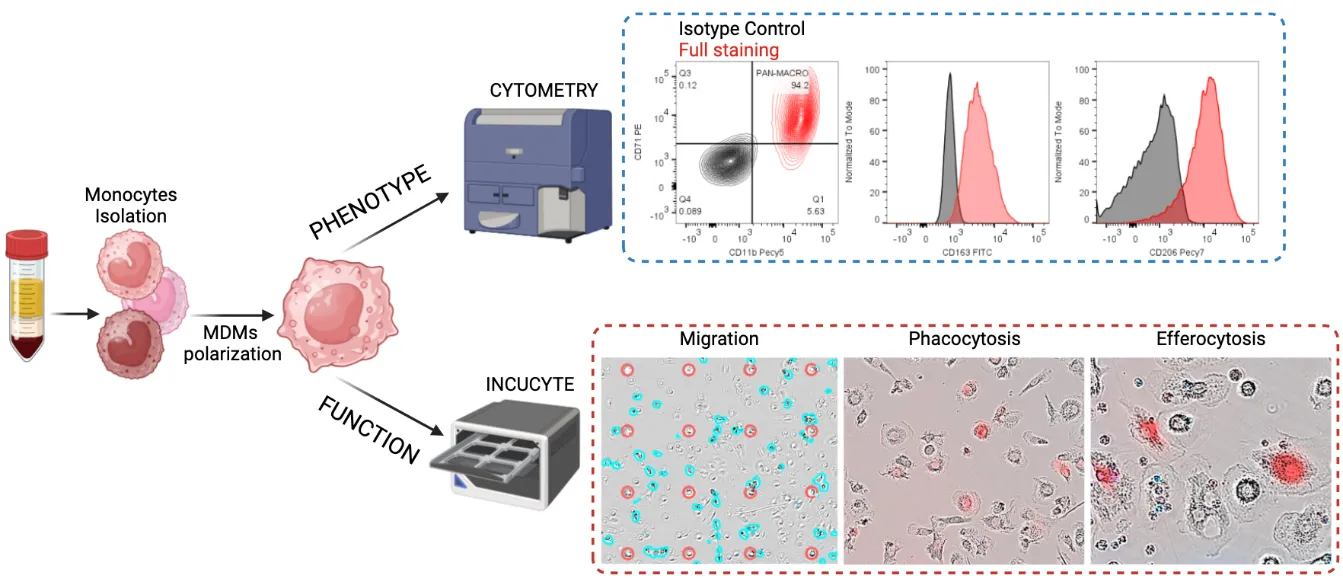
François-Xavier Danlos (Gustave Roussy – Drug Development Department) has created a prospective cohort of over 1000 patients with Immune-Related Adverse Events post Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs) called PREMIS . This includes a large collection of biological samples that are currently being analyzed. FHU CARE² compares the effect of in vitro treatment of anti-TNF, JAKi and Anti-IL-6 on T cells (François-Xavier Danlos) and on monocyte derived macrophages (Audrey Paoletti and Samuel Bitoun) subsets, known to be associated to Immune-Related Adverse Events to compare the potential efficacy of the drugs on various Immune-Related Adverse Events.
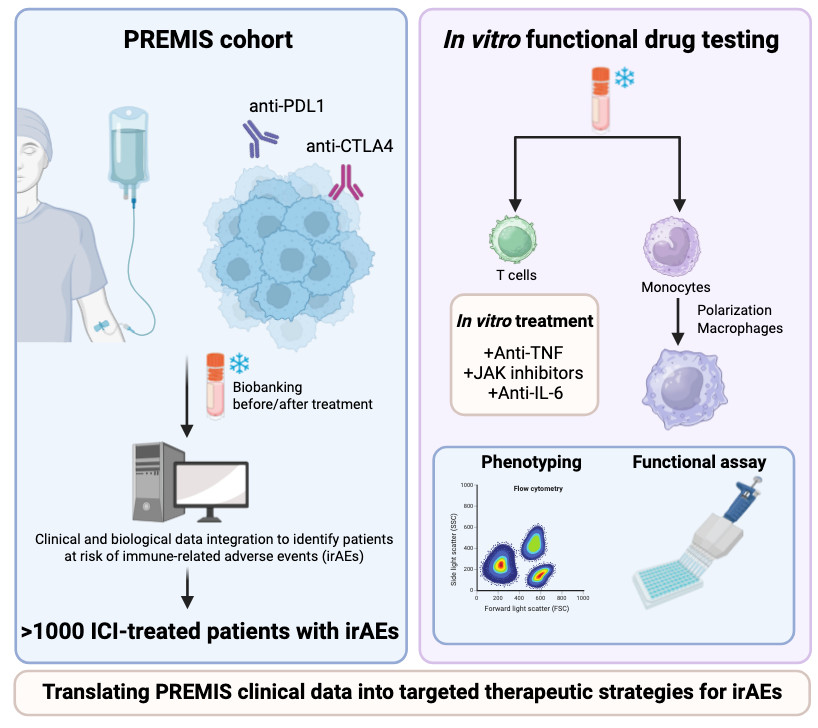
Task 4
To identify mechanisms involved in the curative efficacy and side effects of CAR-T cells and BiTEs therapy in autoimmune diseases and cancers
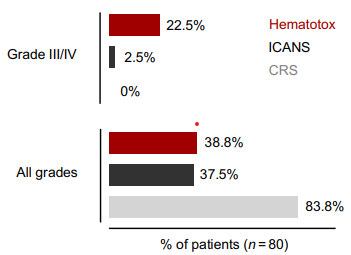
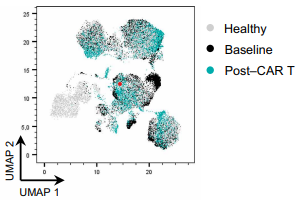
Samuel Bitoun and Camille Bigenwald work together to set up animal models and human cohorts to understand the mechanisms that lead CAR-T cells and BiTEs to cure certain diseases (lymphoma, lupus) and lead to relapse in others, like myeloma. This might allow to understand how to manipulate the immune system with other tools to achieve the same results. Side effects are numerous with these treatments, especially CAR-T cell induce prolonged cytopenia that is difficult to tolerate in autoimmune diseases. Understanding and preventing these effects it is thus a priority. Camille Bigenwald recently developped a mouse model of B cell lymphoma to study the hematotoxic effects of CAR-T cells and described a link between the CAR-T cells abundance in the patient’s bone marrow smears and clonal hematopoiesis.
Laurence Zitvogel (Institut Gustave Roussy, Université de Paris Saclay, INSERM) has published leading papers on the impact of antibiotics in the response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (Routy et al Science 2018, Fidelle et al Science 2023) and is now working on the potential of the microbiome to enhance the efficacy of CAR-T cells in collaboration with Camille Bigenwald.
Read the full scientific article : CAR T cell–mediated bone marrow inflammation causes hematotoxicity and favors clonal hematopoiesis | Science Translational Medicine.